Red Food Coloring Allergy Symptoms A Colorful Conundrum
Common Symptoms of Red Food Coloring Allergies: Red Food Coloring Allergy Symptoms
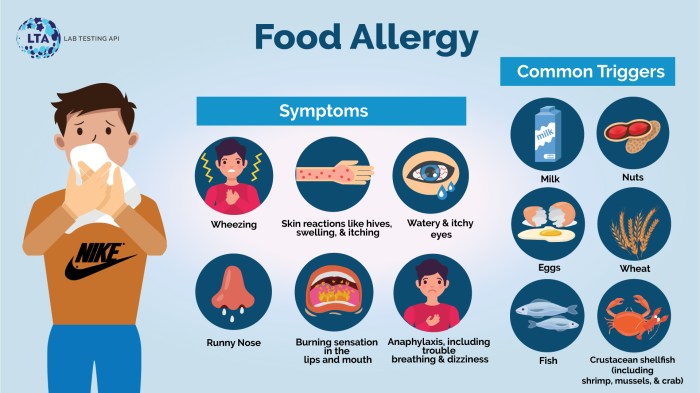
Red food coloring allergy symptoms – Red food coloring allergies, while less common than other food allergies, can manifest in a variety of ways, ranging from mild discomfort to severe reactions requiring immediate medical attention. Understanding the common symptoms, their severity, onset time, and duration is crucial for effective management and prevention. This information is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice.
Always consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment.
Symptom Severity, Onset, and Duration
The following table summarizes common symptoms, their severity, onset time, and duration. It’s important to note that these are general guidelines, and individual experiences can vary significantly.
| Symptom | Severity | Onset Time | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hives (urticaria) | Mild to Severe (depending on size and extent) | Minutes to hours after ingestion | Minutes to days |
| Itching | Mild to Severe | Minutes to hours after ingestion | Minutes to days |
Swelling (angioedema)
|
Mild to Severe (life-threatening if airway is affected) | Minutes to hours after ingestion | Hours to days |
| Rashes | Mild to Severe | Minutes to hours after ingestion | Days to weeks |
| Digestive Issues (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea) | Mild to Severe | Minutes to hours after ingestion | Hours to days |
| Difficulty Breathing (wheezing, shortness of breath) | Severe (life-threatening) | Minutes to hours after ingestion | Minutes to hours (requires immediate medical attention) |
| Anaphylaxis | Severe (life-threatening) | Minutes to hours after ingestion | Variable, requires immediate medical attention |
Mild Versus Severe Allergic Reactions
Mild allergic reactions to red food coloring typically involve symptoms like mild itching, hives, or mild digestive upset. These symptoms are usually manageable with over-the-counter antihistamines. Severe reactions, however, can be life-threatening.
Severe reactions often include swelling of the face, lips, or tongue (angioedema), difficulty breathing, and a sudden drop in blood pressure (anaphylaxis). Anaphylaxis requires immediate emergency medical attention. The difference lies in the intensity and potential for life-threatening complications.
Symptom Variation Based on Individual and Amount Ingested
The symptoms experienced can vary greatly depending on the individual’s sensitivity and the amount of red food coloring ingested. Someone with a mild allergy might only experience itching after consuming a large amount of a product containing red dye, while someone with a more severe allergy could experience a severe reaction from a small amount. For example, one person might develop only a mild rash after eating a single red-colored candy, while another might experience severe anaphylaxis from the same candy.
The concentration of the dye in the food also plays a significant role. A highly concentrated source of red dye is more likely to trigger a reaction, even in individuals with mild sensitivities.
Management and Treatment of Red Food Coloring Allergies
Living with a red food coloring allergy requires a proactive approach to minimize exposure and manage reactions. This involves careful attention to food labels, lifestyle adjustments, and understanding when and how to seek medical assistance. Effective management improves quality of life and prevents potentially serious consequences.
Avoiding Red Food Coloring in Food and Products
Identifying and avoiding sources of red food coloring is crucial. This begins with diligently reading food labels, looking for common artificial colors like Allura Red AC (Red 40), Ponceau 4R (Red 27), and Amaranth (Red 2). Many processed foods, candies, beverages, and even some medications contain these dyes. Beyond food, be mindful of cosmetics, personal care products, and even certain medications which may list these dyes as ingredients.
When eating out, inform restaurant staff about your allergy to ensure they can accommodate your needs and avoid cross-contamination. Choosing fresh, whole foods, prepared at home, minimizes the risk of accidental exposure significantly.
Strategies for Daily Life Management
A well-structured plan helps manage red food coloring allergies effectively. This includes maintaining a detailed food diary to track reactions and potential triggers. This diary can help pinpoint specific foods or products causing allergic responses. Carrying an emergency epinephrine auto-injector (like an EpiPen), if prescribed by a doctor, is vital in case of severe reactions. Educating family, friends, and caregivers about your allergy is essential to ensure they understand the severity and know how to respond in an emergency.
Wearing a medical alert bracelet or necklace clearly indicating your allergy is another important safety precaution.
The Role of Medication in Treating Allergic Reactions
While avoiding exposure is the primary management strategy, medication plays a crucial role in treating allergic reactions. Antihistamines, such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl) or cetirizine (Zyrtec), can alleviate milder symptoms like hives or itching. However, for more severe reactions involving difficulty breathing, swelling of the throat, or dizziness, epinephrine is essential. Epinephrine is a life-saving medication that counteracts the effects of a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis).
It should be administered immediately and followed by immediate medical attention. It is important to note that medication should only be used as directed by a physician. Regular check-ups with an allergist are recommended to monitor the allergy and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Red Food Coloring Allergies in Different Age Groups
Red food coloring allergies manifest differently across age groups, influencing symptom presentation, management strategies, and long-term health implications. Understanding these variations is crucial for effective diagnosis and intervention.
Children and adults often experience overlapping symptoms like hives, itching, and swelling, but the severity and expression can differ significantly. Infants and young children may present with more generalized reactions, including vomiting, diarrhea, and difficulty breathing, requiring immediate medical attention. Adults, while experiencing similar symptoms, might exhibit more localized reactions or less severe gastrointestinal distress. Management approaches also vary, with children requiring careful monitoring and possibly epinephrine auto-injectors, while adults may manage milder reactions with antihistamines.
Symptom Differences Between Children and Adults
While both age groups can experience skin reactions (urticaria, angioedema), gastrointestinal issues (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea), and respiratory problems (wheezing, difficulty breathing), the presentation varies. Children often show more severe and widespread reactions, possibly due to their developing immune systems and smaller body mass. For example, a small amount of red food coloring in a child’s snack might trigger a severe reaction, while the same amount might cause only mild discomfort in an adult.
Adults may have developed tolerance to certain levels of exposure over time, leading to less severe reactions, although this is not always the case.
Management Strategies Across Age Groups
Management focuses on avoidance of red food coloring, which is the cornerstone of treatment. However, implementation differs. For children, careful scrutiny of food labels and proactive communication with caregivers and educators is vital. Adults often have more control over their diet, but meticulous label reading remains essential. Antihistamines can alleviate symptoms in both groups, but the dosage and type will be adjusted based on age and weight.
Epipen administration training is often recommended for children with severe allergies, ensuring rapid response in case of anaphylaxis.
Long-Term Health Implications of Untreated Allergies
Untreated red food coloring allergies can lead to several long-term consequences. Repeated exposure can increase the risk of developing more severe reactions over time, potentially leading to anaphylaxis, a life-threatening condition. Chronic gastrointestinal distress can also lead to malnutrition and other complications. Furthermore, untreated allergies can significantly impact quality of life, restricting dietary choices and causing anxiety surrounding food consumption.
Red food coloring allergies can manifest in hives, itching, or even swelling. This sensitivity isn’t limited to humans; wondering if your furry friend is reacting too? Check out this article on whether or not does food coloring irritate dogs skin , as similar reactions can occur in pets. Understanding these reactions helps us better manage potential allergic responses to red food coloring in both ourselves and our animal companions.
Early intervention is critical to prevent these long-term effects.
Importance of Early Diagnosis and Intervention, Red food coloring allergy symptoms
Early diagnosis is paramount in managing red food coloring allergies effectively. Prompt identification allows for the implementation of avoidance strategies and appropriate medical management. This reduces the risk of severe reactions and minimizes the long-term health impact. If a child or adult experiences symptoms after consuming foods containing red food coloring, immediate consultation with an allergist is crucial.
Skin prick tests or blood tests can confirm the allergy, allowing for personalized management plans. Early intervention not only protects against severe reactions but also empowers individuals and families to manage their allergies proactively.
Illustrative Examples of Red Food Coloring Allergy Reactions
Allergic reactions to red food coloring, primarily Allura Red AC (also known as Red 40), can manifest in a wide spectrum of severity. Understanding these variations is crucial for proper diagnosis and management. The following examples illustrate the diverse ways individuals can react.
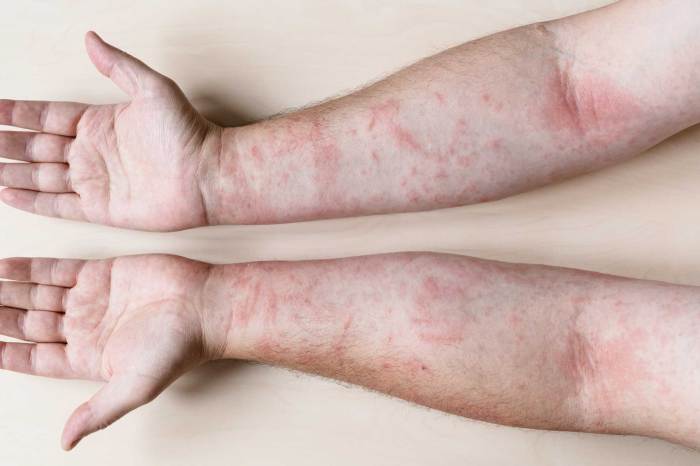
Mild Allergic Reaction: Skin Rash
Six-year-old Lily consumed a strawberry-flavored yogurt containing Allura Red AC. Within an hour, she developed a mild, itchy rash on her cheeks and neck. The rash was characterized by small, red bumps and some mild swelling. No other symptoms were present. After removing the potential allergen from her diet and applying a topical hydrocortisone cream, the rash subsided within 24 hours.
This case exemplifies a common, relatively benign reaction. The trigger was clearly identified, and the symptoms resolved quickly with simple management.
Moderate Allergic Reaction: Gastrointestinal Distress
A 25-year-old man, Mark, ate a slice of red velvet cake at a birthday party. Two hours later, he experienced significant gastrointestinal distress, including nausea, vomiting, and abdominal cramping. He also reported diarrhea. These symptoms lasted for approximately six hours before gradually subsiding. Mark did not experience any respiratory or skin manifestations.
This moderate reaction highlights how the digestive system can be a primary site of reaction to red food coloring. The temporal relationship between cake consumption and symptom onset strongly suggests Allura Red AC as the culprit.
Severe Allergic Reaction: Anaphylaxis
A 12-year-old girl, Sarah, consumed a candy containing Allura Red AC. Within minutes, she experienced a rapid onset of symptoms including hives, swelling of her lips and tongue (angioedema), and difficulty breathing. Her mother immediately administered her epinephrine auto-injector (EpiPen), and called emergency services. Sarah was transported to the hospital where she received further treatment, including intravenous fluids and monitoring.
This severe reaction, demonstrating anaphylaxis, showcases the potential life-threatening nature of red food coloring allergies. The rapid progression and involvement of multiple systems underscore the need for immediate medical intervention in such cases. The prompt use of the EpiPen likely prevented a fatal outcome.
FAQ Explained
Can I have a red food coloring allergy and not react to all red dyes?
Absolutely! Different red dyes have different chemical structures, and an allergy to one doesn’t automatically mean you’re allergic to them all. It’s a matter of which specific molecules your immune system identifies as a threat.
Are red food coloring allergies more common in children or adults?
While allergies can develop at any age, they often manifest in childhood. However, adults can also develop red food coloring allergies later in life.
How long do symptoms of a red food coloring allergy typically last?
This varies wildly depending on the severity of the reaction and the treatment received. Mild reactions might clear up in a few hours, while more severe reactions may require medical intervention and last longer.
What’s the difference between a red food coloring allergy and an intolerance?
An allergy involves the immune system, triggering a potentially life-threatening reaction. An intolerance is a digestive issue causing discomfort but not a full-blown immune response.
